Tests & Consultation
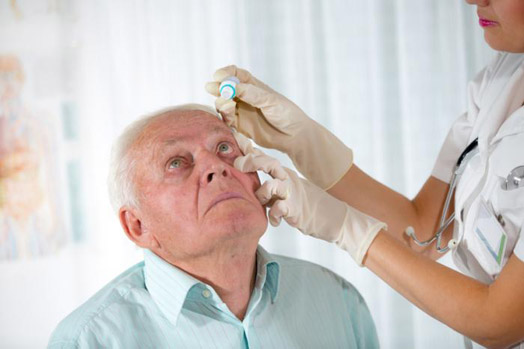
Pupil Dilation
To obtain a better view of the eye’s internal structures, your eye doctor instills dilating drops to enlarge your pupils. Dilating drops usually take about 15 to 30 minutes to start working. When your pupils are dilated, they will be sensitive to light (because more light is getting into your eye) and you may notice difficulty focusing on objects up close. These effects can last for up to several hours, depending on the strength of the drop used. Once the drops have taken effect, your eye doctor will use various instruments to look inside your eyes. Be aware that you will be not able to drive a car on your way back home. Because driving safely may not be possible after having your eyes dilated, you should make arrangements to have someone drive you after your appointment. You should bring sunglasses with you to minimize glare and light sensitivity when you leave your appointment.
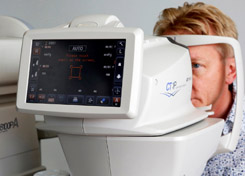
Refraction: vision, visual acuity, contrast, glasses strength
Among the first tests performed in a comprehensive eye exam are visual acuity tests that measure the sharpness of your vision. This is the test that your eye doctor uses to determine your best visual acuity and glasses strength. These usually are performed using a projected eye chart to measure your distance visual acuity and a small, hand-held acuity chart to measure your near vision. In the computerised test, you look through a machine that measures the amount of light reflected by your retina. The results of the test can help diagnose the eye conditions.
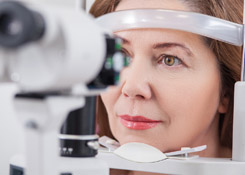
Slit lamp exam
A slit lamp is a binocular microscope (or “biomicroscope”) that your eye doctor uses to examine the structures of your eye under high magnification. During the slit lamp exam, you will be asked to place your forehead and chin securely against the rests on the front of the instrument and your doctor will begin by examining the structures of the front of your eyes — including your eyelids, cornea, conjunctiva, iris and lens. The binocular slit-lamp examination provides a stereoscopic magnified view of the eye structures in detail, enabling anatomical diagnoses to be made for a variety of eye conditions.
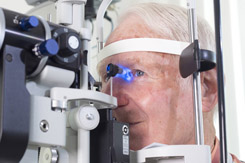
Intraocular pressure measurement - Tonometry
Tonometry test is an exam to measure your intraocular pressure. For this test, your eye doctor will put yellow eye drops in your eye to numb it. Your eyes will feel slightly heavy when the drops start working. This is not a dilating drop — it is a numbing agent combined with a yellow dye that glows under a blue light. Then the doctor will have you stare straight ahead into the slit lamp while he or she gently touches the surface of your eye with the tonometer to measure your intraocular pressure. The applanation tonometry is painless. The whole test takes just a few seconds.
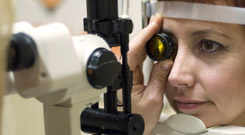
Fundoscopy
With the slit lamp exam and help of a hand-held lens, your doctor may also use the slit lamp to examine structures located further back in the eye, such as the retina and optic nerve. For this test, your eye doctor will put dilating eye drops in your eyes to make your pupils wider. Fundoscopy, especially when the pupils are dilated for a more complete view of the entire retina, allows for examination of the retina to help diagnose conditions and identify risk factors for potential vision loss associated with the retina.
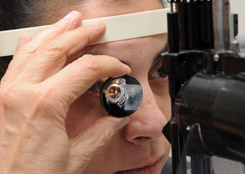
Gonioscopy
Gonioscopy is an eye examination to look at the front part of your eye (anterior chamber) between the cornea and the iris. Gonioscopy is a painless examination to see whether the area where fluid drains out of your eye (called the drainage angle) is open or closed. It is often done during a regular eye examination, depending on your age and whether you are at high risk for glaucoma. Eyedrops are used to numb your eye so that you will not feel the lens touching your eye during this painless examination. A special lens is placed lightly on the front of your eye, and a narrow beam of bright light is pointed into your eye.
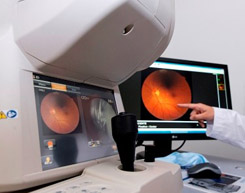
Retinography
Digital retinography also known as fundus photography is the creation of a photograph of the interior surface of the eye, including the retina, optic disc, macula, and posterior pole. Fundus photography is used for monitoring progression of a disease, diagnosis of a disease or in screening programs and epidemiology.
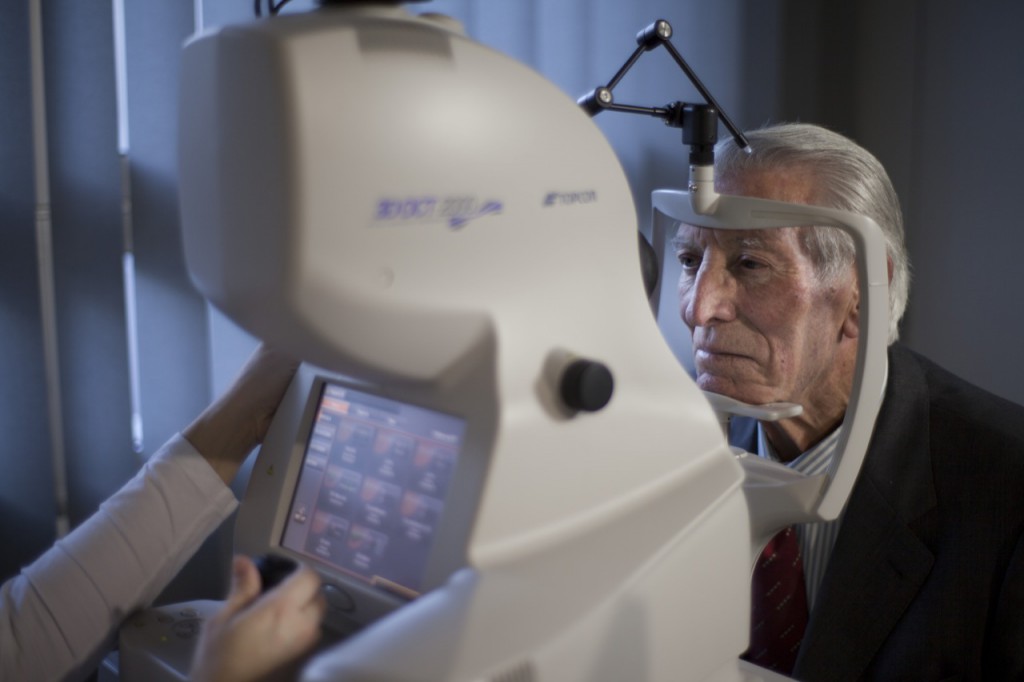
OCT macula scan
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test that uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of your retina, the light-sensitive tissue lining the back of the eye. OCT is useful in the diagnosis of many retinal conditions, especially lesions in the macula. OCT can be particularly helpful in diagnosing: macular hole, macular pucker, vitreomacular traction, macular edema, detachments of the neurosensory retina and retinal pigment epithelium (e.g. central serous retinopathy or age-related macular degeneration.
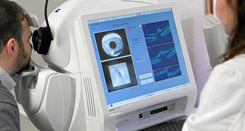
OCT optic nerve scan
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test that uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of the back of the eye. OCT is very precise when evaluating optic nerve disorders such as glaucoma. The scan of the optic nerve can accurately and reproducibly evaluate the nerve fiber layer thickness.
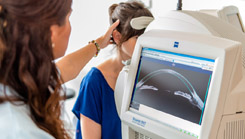
OCT anterior segment scan
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test that uses light waves to take cross-section pictures of the eye and gives detailed images of the anterior segment: cornea, anterior chamber, iris and angle. The high-resolution images show the layers of the cornea, anterior chamber angle and images of scleral structures.
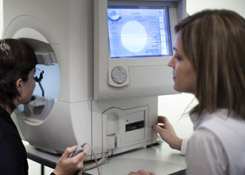
Visual field
A visual field test is an eye examination that can detect dysfunction in central and peripheral vision which may be caused by various medical conditions such as glaucoma, stroke, brain tumours or other neurological deficits. The test is a method of measuring an individual’s entire scope of vision, that is their central and peripheral (side) vision. Visual field tests are used to detect blind spots (scotomas), which could be a sign of eye diseases. The size and shape of a scotoma offer important clues about the presence and severity of diseases of the eye, optic nerve and visual structures in the brain.
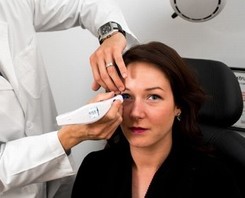
Pachymetry
A pachymetry test is a simple, quick, painless test to measure the thickness of your cornea. With this measurement, your doctor can better understand your intraocular pressure reading, and develop a treatment plan that is right for your condition. The procedure takes only about a minute to measure both eyes.
Corneal pachymetry is considered an important test in the early detection of glaucoma and it is essential for other corneal surgeries
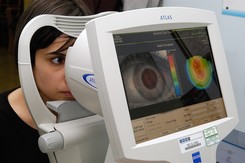
Corneal topography
Corneal topography is a non-invasive medical imaging technique for mapping the surface curvature of the cornea, the outer structure of the eye. The three-dimensional map is therefore a valuable aid to the examining and can assist in the diagnosis and treatment of a number of conditions; in planning cataract surgery and intraocular lens implantation, in planning refractive surgery such as LASIK, and evaluating its results; or in assessing the fit of contact lenses.
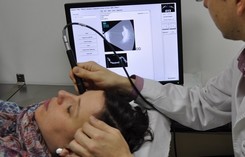
B-scan ultrasonography
The ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves that travel through the eye. Reflections (echoes) of the sound waves form a picture of the structure of the eye. B-scan is done to look at the inside part of the eye or the space behind the eye that can’t be seen directly. This may occur when you have cataracts or other conditions that make it hard for the doctor to see into the back of your eye. The test may help diagnose retinal detachment, tumors, or other disorders.
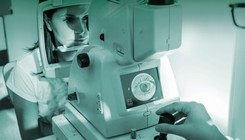
Biometry eye test
A biometry eye test is an examination to measure eye length and the power of the cornea. Data from a biometry test is used to calculate the correct power of intraocular lens implants. After cataract or refractive surgery, it is essential to implant an intraocular lens with the best refractive power into the individual’s eye. An accurate biometry eye test yields data that are used to determine the ideal power of the intraocular lens that gives the best refraction.

